Table of contents
- 1. FromSqlRaw Method Support
- 2. Translation of Distinct method
- 3. Time-to-live Configuration
- 4. Throughput Configuration
- 5. Resolving HTTP Client Factory
- 6. Supporting Collections of Primitive Types
- 7. Default to Implicit Ownership
- 8. Diagnostics Improvements
- 9. String Methods Translations
- 10. Math/MathF Methods Translations
- Wrapping Up
1. FromSqlRaw Method Support
In EF Core 6.0, Cosmos DB provider supports the FromSqlRaw method. It works in the same way as relational providers.
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var query = context.Posts
.FromSqlRaw("SELECT * FROM Posts")
.ToQueryString();
Console.WriteLine(query);
// SELECT c
// FROM (
// SELECT * FROM Posts
// ) c
class Post
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ExampleDB");
}
2. Translation of Distinct method
In EF Core 6.0, Cosmos DB provider now translates Distinct method in simple queries.
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var query = context.Posts
.Select(p => p.Rating)
.OrderBy(r => r)
.Distinct()
.ToQueryString();
Console.WriteLine(query);
// SELECT DISTINCT c["Rating"]
// FROM root c
// WHERE (c["Discriminator"] = "Post")
// ORDER BY c["Rating"]
class Post
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public int Rating { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ExampleDB");
}
3. Time-to-live Configuration
In EF Core 6.0, entity types in the Cosmos model can be configured with the default time-to-live and time-to-live for the analytical store.
class Post
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public int Rating { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder
.Entity<Post>(entityTypeBuilder =>
{
entityTypeBuilder.HasDefaultTimeToLive(100);
entityTypeBuilder.HasAnalyticalStoreTimeToLive(200);
});
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ExampleDB");
}
4. Throughput Configuration
In EF Core 6.0, you can configure manual or auto-scale throughput for Cosmos DB. You can do it on the database or for the corresponding container.
class Post
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public int Rating { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
// Provision throughput on the database
modelBuilder.HasManualThroughput(2000);
modelBuilder.HasAutoscaleThroughput(6000);
// Provision throughput for the corresponding container
modelBuilder
.Entity<Post>(entityTypeBuilder =>
{
entityTypeBuilder.HasManualThroughput(3000);
entityTypeBuilder.HasAutoscaleThroughput(12000);
});
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ExampleDB");
}
5. Resolving HTTP Client Factory
In EF Core 6.0, for Cosmos DB provider, you can explicitly set the HttpClientFactory. It's helpful during testing. For instance, to bypass certificate validation when using the Cosmos DB emulator on Linux.
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ExampleDB",
cosmosOptionsBuilder =>
{
cosmosOptionsBuilder.HttpClientFactory(
() => new HttpClient(
new HttpClientHandler
{
ServerCertificateCustomValidationCallback =
HttpClientHandler.DangerousAcceptAnyServerCertificateValidator
}));
});
}
6. Supporting Collections of Primitive Types
Cosmos DB provider supports collections of primitive types in EF Core 6.0. Lists and dictionaries can be populated, inserted, and updated in the normal way.
However, only dictionaries with string keys are supported, and you cannot query the contents of collections.
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var book = new Book
{
Title = "Some book",
Quotes = new List<string> { "Some quote" },
Notes = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{ "12", "Some note"},
{ "234", "Another note"}
}
};
context.Books.Add(book);
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
book = context.Books.First();
book.Quotes.Add("New quote");
book.Notes["12"] = "Updated note";
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
class Book
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public IList<string> Quotes { get; set; }
public IDictionary<string, string> Notes { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ExampleDB");
}
7. Default to Implicit Ownership
In EF Core 6.0, when building the Cosmos model, you don't need to mark child entities as owned by their parents. EF Core will do it for you by default.
You have to use OwnsOne/OwnsMany methods only if you need a further configuration of owned types.
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var blog = new Blog
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
Name = "Oleg's Blog",
NavBarItems = new List<NavBarItem>
{
new NavBarItem { Name = "Home", Url = "/home" },
new NavBarItem { Name = "About", Url = "/about" }
},
Posts = new List<Post>
{
new Post
{
Title = "Hello World",
Content = "Content",
Tags = new List<Tag>
{
new Tag { Name = "Tag1" },
new Tag { Name = "Tag2" }
}
}
}
};
context.Add(blog);
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
class Blog
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public IList<NavBarItem> NavBarItems { get; set; }
public IList<Post> Posts { get; set; }
}
class NavBarItem
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Url { get; set; }
}
class Post
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
public IList<Tag> Tags { get; set; }
}
class Tag
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Blog>()
.HasPartitionKey(e => e.Name);
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "ImplicitOwnershipsDB");
}
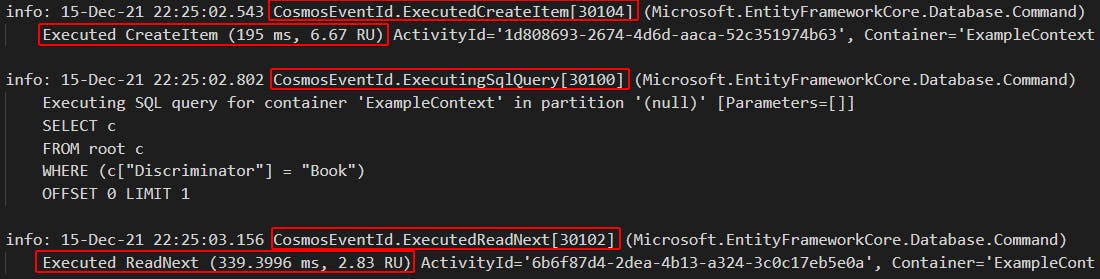
8. Diagnostics Improvements
In EF Core 6.0, the Cosmos DB provider logs more diagnostic information. It logs events for inserting, querying, updating, and deleting data. It also includes the request units (RU).
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var book = new Book
{
Title = "Some book"
};
context.Books.Add(book);
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
book = context.Books.First();
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
class Book
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options
.EnableSensitiveDataLogging()
.LogTo(Console.WriteLine)
.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "DiagnosticsDB");
}
Output:
9. String Methods Translations
In EF Core 6.0, the Cosmos DB provider translates more String methods.
Translated methods:
- String.Length -> LENGTH
- String.ToLower -> LOWER
- String.TrimStart -> LTRIM
- String.TrimEnd -> RTRIM
- String.Trim -> TRIM
- String.ToUpper -> UPPER
- String.Substring -> SUBSTRING
- '+' operator -> CONCAT
- String.IndexOf -> INDEX_OF
- String.Replace -> REPLACE
- String.Equals -> STRINGEQUAL
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var query = context.Posts
.Where(p => p.Title.ToUpper() == ".NET"
|| p.Title.ToLower() == "hello world"
|| p.Title.Length > 10)
.ToQueryString();
Console.WriteLine(query);
// SELECT c
// FROM root c
// WHERE ((c["Discriminator"] = "Post")
// AND(((UPPER(c["Title"]) = ".NET")
// OR(LOWER(c["Title"]) = "hello world"))
// OR(LENGTH(c["Title"]) > 10)))
class Post
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "StringTranlationsDB");
}
10. Math/MathF Methods Translations
In EF Core 6.0, the Cosmos provider translates Math/MathF methods.
Translated methods:
- Abs -> ABS
- Acos -> ACOS
- Asin -> ASIN
- Atan -> ATAN
- Atan2 -> ATAN2
- Ceiling -> CEILING
- Cos -> COS
- Exp -> EXP
- Floor -> FLOOR
- Log -> LOG
- Log10 -> LOG10
- Pow -> POWER
- Round -> ROUND
- Sign -> SIGN
- Sin -> SIN
- Sqrt -> SQRT
- Tan -> TAN
- Truncate -> TRUNC
using var context = new ExampleContext();
var query = context.Products
.Where(p => Math.Abs(p.Price) == 100
|| Math.Round(p.Price) > 100)
.ToQueryString();
Console.WriteLine(query);
// SELECT c
// FROM root c
// WHERE ((c["Discriminator"] = "Product")
// AND((ABS(c["Price"]) = 100.0)
// OR(ROUND(c["Price"]) > 100.0)))
class Product
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
class ExampleContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Product> Products { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder options)
=> options.UseCosmos(
"https://localhost:8081",
"[key]",
databaseName: "MathTranlationsDB");
}
Wrapping Up
All code samples you can find on my GitHub.

